Six key biosecurity factors must be efficiently managed to manage IBD appropriately.
Infectious bursal illness (IBD) is an acute viral an infection for younger rooster (broiler and pullets) brought on by the IBD virus (IBDV), labeled within the Birnaviridae household, genus Avibirnavirus
(Eterradossi and Saif 2020). This virus is non-enveloped, with 2 segments of RNA and a really resistant capsid, making it a resident pathogen in a farm. Cleansing and disinfection are key to lower the IBDV strain and to cease the Gumboro cycle. This process must be related to a strict farm isolation and an tailored vaccination program which protects the immune system from an infection.
Six key biosecurity factors must be efficiently managed to manage IBD appropriately.
1. Find out how to create a clear space:
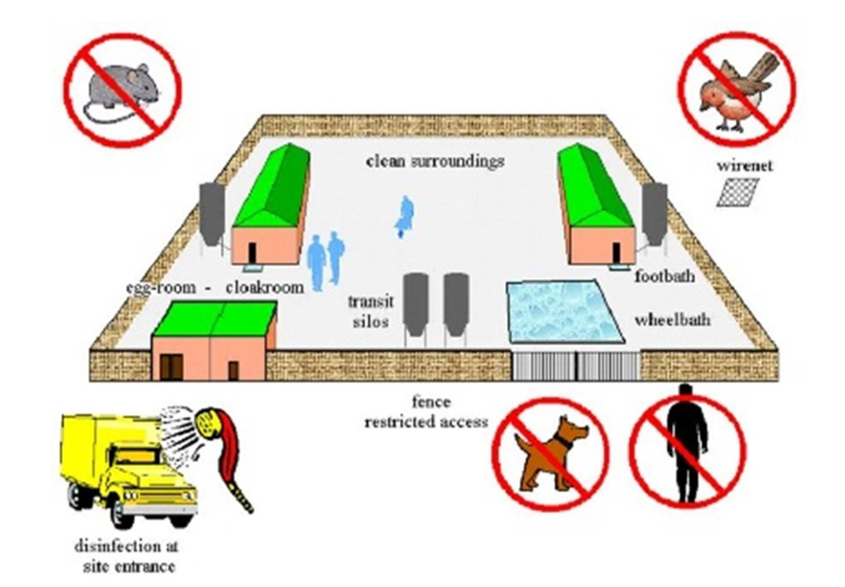
Across the farm, partitions or wired fences separate exterior and inner farm areas, thus creating an epidemiological unit. This unit have to be remoted and secured (fig. 1). The staff and guests should take a bathe and use farm-specific PPE (boots, general, gloves, masks, hairnet) to work contained in the farm. For IBDV, the upper danger of exterior contamination are palms, boots, and dirt round any home entrance (e.g. gates on the home entrance for day-old chicks and litter placement and doorways at each side to entry the gear and management room). The realm across the cooling pad space can also be crucial for mud accumulation (fig 2). The gear and management room of every home have to be divided into 2 zones, every zone utilizing its personal pair of shoes, recognized with completely different colors (outer space and inside space).
2. Find out how to keep away from vectors coming into the farm/home:
Rodents and bugs (darkling beetles, flies) are thought-about a dynamic vector of IBDV, since they transfer round completely different farms & homes, are a possible reservoir of IBDV in the home in turnaround instances.
Rodent’s management: Rodents might be current wherever. Set a bait with rodenticide each 10 meters round the home, storage room, workplace, and so on. File the outcomes (bait consumed or unconsumed) and alter the rodenticide bait each month. It ought to comprise difenacoum or brodifacum as energetic ingredient. All feed residues have to be totally cleaned, particularly below the feed silos.
Flies’ management: Flies just like the scent of feed and shade (pink, yellow) (fig. 3). To seize grownup flies, use pesticides (thiamethoxam, permethrin
or neonicotinoid) and intercourse pheromone baits (tricosene as instance) + sugar. Mixing 5 g. of insecticide with 3 water droplets in a recipient is sufficient to management flies in 50m². To establish moist aera (litter below water pipeline, flooring within the nook have to be dry.
Darkling beetles’ management: as soon as the final broiler leaves the home, the darkling beetles cover rapidly in wall cracks or areas with onerous entry (fig. 4). You may have only some minutes to spray a concentrated answer of insecticide containing pyrethroids (tetramethrin), pseudo pyrethroids (Etofenprox), Nicotinoids (Acetamiprid) or spinosad on 50 centimeters across the wall-floor junctures. Cracks and holes within the flooring and the partitions have to be crammed. Round 80 L. of answer is sufficient to spray a flooring perimeter of 1000 m², for instance.
3. Litter administration:
1 gr. of used litter would possibly comprise as much as 106 viruses. At clean-out, all mud ensuing from litter elimination have to be cleaned as much as tremendously lower viral problem. Ideally, use conveyors tunnels product of plexiglass directed to vans with a trailer cowl. Watch out with the wind currents. The ground have to be cleaned with computerized sweeper (if accessible) and manually (image n°4). For grime flooring, quicklime powder from the earlier cycle would assist whereas cleansing up litter residues.
4: Cleansing and disinfection protocols (all surfaces, together with minor gear):
The target of a cleansing compound is to cut back the quantity of biofilm on the floor. Acid cleaners are used in opposition to mineral supplies and enzymatic cleaners in opposition to natural materials; nonetheless, fundamental cleaners are most successfully sprayed with a foam-gun (fig. 5). After half-hour of contact time, the contact surfaces have to be rinsed with excessive strain water.
Making use of the disinfectant: One should calculate the developable floor by including up all the weather contained in the house we have to disinfect.
E.g.: Developable floor (m2) = flooring + wall + roof + gear + cooling pad + fan + pipeline + feed line + plates.
This calculation would possibly range, relying on which materials the home is product of or comprises (concrete, slate flooring, or cages). The developable floor would then range accordingly, between 3-44 instances greater than a daily concrete flooring home (this coefficient calculation is obtainable, ask our native staff).

Dosage: Disinfectant suppliers usually describe the % of disinfectant wanted to inactivate a virus (utilizing particular virucidal efficacy checks throughout conformance processes). If the IBD virus exercise is 1%, we must always spray 3 ml. of disinfectant per m². Multiply this by the quantity of developable floor (calculated above) and you’ll acquire the required quantity of disinfectant wanted. Relying on the floor’s liquid retention capability, you would possibly have to estimate the amount of water required to humidify all surfaces, to not get in need of answer.
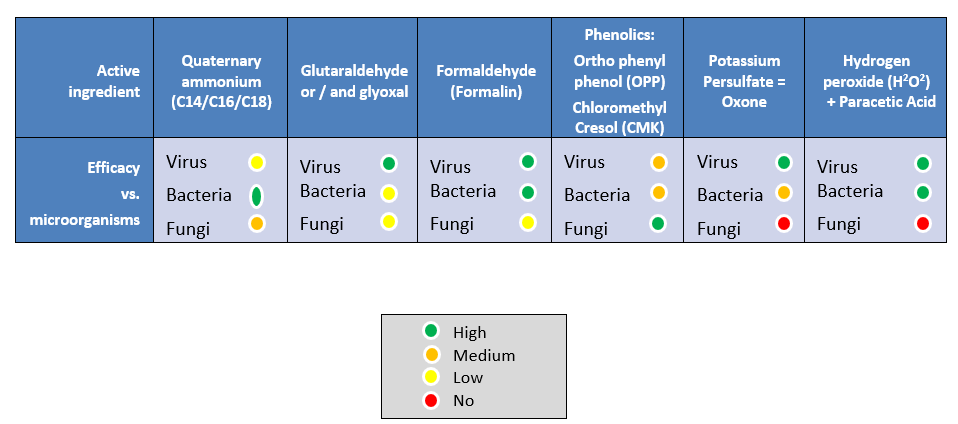
Disinfectant selection: Glutaraldehyde-quaternary ammonia; oxidizers, phenolics are efficient if the contact time is sufficient and an acceptable amount of disinfectant is sprayed on all surfaces. It is very important make a correct cleansing and disinfection of the wall-base as a result of this a part of the wall is in direct contact with day-old chicks and litter residues would possibly stay uncleaned. Disinfectant exercise reduces 5 logs of IBDV every half-hour.
Minor gear might be cleaned and disinfectedcted in a specif a selected(exterior the home) utilizing a selected protocol. Firstly, take away the natural materials connected by brushing it and place it in a cleaner tank. After half-hour of contact time, rinse it and add the disinfectant answer. Let it dry out on a selected space.
5: Ground disinfection (e.g. home 1000 m²)
A sodium hydroxide answer (100 kg. / 500 L. water) might be utilized on the ground, anticipating a 2-15 mm. of penetration throughout the materials. After 6 hours, apply 250 kg. of quicklime powder (doubling the dose for earthen flooring) and spray water for activation (200-600 L.)
Down time interval definition: Time spent between cleansing and disinfected of all surfaces and the brand new litter and the gear is positioned once more. An efficient downtime interval might be maximally diminished to some days (2-4 days, to ensure that all surfaces are dry).
Particular case of the slat: To optimize effectivity of slat disinfection, the slat are disinfected exterior in a selected space (as small gear).
Protocol:
- seaking in water tank
- brushing
- cleaner tank with detergent
- contact time space 30minutes
- rincing;
- disinfectant tank
- drying space + storage.
6. Litter placement (or slat positioning).
The litter (with good high quality uncooked materials: no mud) reduces the chance of contact between the DOC’s and the ground (thought-about the main virus reservoir). A thickness of 10 cm. of litter is really useful for good safety, liquid retention, and to keep away from fermentation. Litter turning might be harmful as a result of the virus would possibly then be uncovered to the floor and are available shut contact with the birds.
Conclusion:
A correct cleansing and disinfection protocol is crucial to lower the IBDV load throughout the downtime interval and simply earlier than new placement of day-old chicks. The effectivity of this protocol might be challenged by wasp (resistant tissu fabric) and IBDV qPCR 2 days after disinfection. Disinfectant neutralizers have to be used throughout sampling and on the laboratory to reduce false destructive outcomes.
A secondary fogging disinfection after litter placement is non-obligatory to safe disinfection (attention-grabbing in cage or slat manufacturing) however it is suggested when IBDv strain is excessive for instance in previous homes or in massive complexes.

