Mycoplasma synoviae is among the commonest preconditions for secondary bacterial infections in poultry. It causes subclinical infections of the higher respiratory tract, which might turn into systemic infections and lead to diminished and poor-quality egg manufacturing.
In such circumstances, Gallibacterium anatis as an opportunistic pathogen usually causes medical infections characterised by melancholy, diarrhea, respiratory syndrome and decreased egg manufacturing. The goal of this research was to find out doable correlation within the prevalence of G. anatis and M. synoviae, in addition to mutual correlation of their amount. The analysis was carried out on sixteen layer flocks from eight completely different farms. The tracheal swab samples have been analyzed utilizing qPCR assay. The outcomes confirmed statistically vital correlation within the analyzed samples relating to the prevalence of each pathogens on the farms, with considerably greater common ranges of G. anatis in comparison with M. synoviae. No correlation relating to amount of every pathogen was detected.
Introduction
Infections attributable to Gallibacterium anatis (G. anatis) and Mycoplasma synoviae (M. synoviae) can result in nice financial losses within the poultry manufacturing. M. synoviae is among the commonest preconditions for secondary infections, whereas G. anatis simply spreads from the higher to decrease elements of the respiratory system or ascendingly by way of the oviduct to the coelomic cavity, and causes extreme infections.
G. anatis is an opportunistic pathogen that may trigger medical infections characterised by melancholy, diarrhea, respiratory syndrome and decreased egg manufacturing. Nonetheless, the an infection is steadily subclinical and simply neglected. There are numerous predisposing elements reminiscent of impaired immunity, hormonal standing, stress, poor zoohygienic circumstances and coinfections, which might result in systemic infections and excessive mortality charges. The morbidity and mortality charges fluctuate in naturally contaminated animals, whereas in experimentally contaminated immunosuppressed layers the mortality can improve as much as 73%. As a result of inadequacy of the standard diagnostic strategies for detection of G. anatis, the pathogen is usually tough to isolate and due to this fact misdiagnosed. Consequently, a extremely particular, delicate and reproducible qPCR technique was developed, which was additionally used on this research in an effort to determine and quantify the pathogen.
M. synoviae causes subclinical an infection of the higher respiratory tract, which might result in secondary respiratory and systemic infections. It may additionally trigger decreased egg high quality and manufacturing, in addition to lameness and extreme arthritis. M. synoviae strains have tropism for various tissues, however the synergism between arthrotropic and salpingotropic strains and different respiratory pathogens has been documented in a number of research. Versus the respiratory and arthropathic types, the final 20 years strains with oviduct tropism, that are related to egg deformities, have been more and more detected. Respiratory type of the illness could be characterised by rales, however is mostly asymptomatic. Morbidity in hen flocks varies between 2 and 75%, whereas mortality is normally lower than 1%, which consequently leads to excessive condemnations, decreased weight positive aspects and feed effectivity. Industrial ELISA assays are sometimes used for routine flock monitoring, whereas the identification is completed utilizing completely different PCR-based strategies.
Each micro organism are mostly positioned within the higher respiratory system and steadily trigger subclinical infections, due to this fact the goal of this research was to find out their prevalence, in addition to mutual correlation of their amount within the studied laying hen flocks.
Supplies and strategies
Sampling and DNA isolation
On this research, sixteen flocks from eight laying hen farms have been investigated. The age of the flocks diversified from 8 to 66 weeks of age (Desk 1). 5 tracheal swabs per flock have been sampled and saved at -20 °C till the DNA isolation. DNA was remoted from each pattern individually utilizing the GenElute Mammalian Genomic DNA Miniprep Equipment (Sigma-Aldrich, Co., St Louis, MO, USA) in accordance with the producer’s directions. Remoted DNA was saved at -20 °C till additional evaluation.
qPCR analyses
Quantification of the micro organism was carried out utilizing GoTaq Probe qPCR Grasp Combine (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Used primers and probes have been particular for G. anatis (gyrB: F-5’-CGATTGTGTCCGTTAAAGTGC, R-5’-TGCAAACGCTCACACCAACTG, P-5’-FAM-CTGGTTTCTTCCGAAGTGAAAAGTGTAGTGGA-BHQ1) and M. synoviae (16S-23S rDNA ISR: F-5’-CTAAATACAATAGCCCAAGGCAA, R-5’-CCTCCTTTCTTACGGAGTACA, P-5’-FAM-AGCGATACACAACCGCTTTTAGAAT-BHQ1). Quantification protocols have been carried out as described by Wang et al. (2016), and Raviv and Kleven (2008). The full quantity of the response combination was 15 µL. Every pattern was analyzed in duplicate, whereas G. anatis and M. synoviae samples of identified focus have been carried out in triplicate in parallel for the aim of absolute quantification. The analyses have been carried out utilizing Mx3005P instrument (Stratagene, USA).
Statistical evaluation
The statistical analyses have been carried out in Statistica 13.5.0.17. (TIBCO Software program Inc.) software program. The conventional distribution was examined utilizing Kolmogorov-Smirnov check, and the common variety of genome copies was examined utilizing Mann-Whitney U check. Correlation between the pathogen copy quantity and the correlation between the prevalence of each pathogens on every farm have been analyzed utilizing correlation matrices. Statistical significance was set at degree p<0.05.
Outcomes
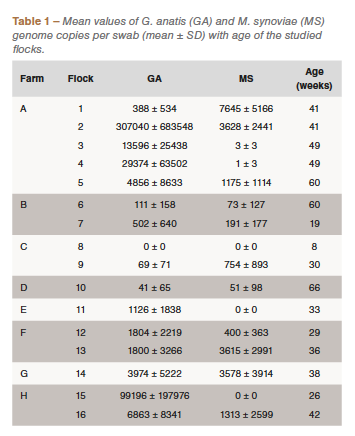
Each pathogens have been detected within the majority of the studied flocks, except Flock 11 (Farm E) and Flock 15 (Farm H) the place M. synoviae was not detected, and Flock 8 (Farm C) the place not one of the pathogens was detected, presumably due to the younger age of the flock (Desk 1). The outcomes confirmed greater imply copy numbers per pattern for G. anatis, usually (Desk 1), and a considerably greater common copy variety of G. anatis on all farms (information not proven). There was no correlation between the pathogens in regard to the amount of micro organism per swab (Determine 1A). Nonetheless, outcomes confirmed statistically vital correlation (p = 0.032) within the prevalence of G. anatis and M. synoviae (Determine 1B).
 Dialogue
Dialogue
The target of this research was to find out the doable correlation within the prevalence of G. anatis and M. synoviae, and mutual correlation of their amount within the tracheal swabs of laying hens. Each micro organism colonize the respiratory system, which can lead to medical infections with excessive manufacturing losses. A number of research have proven that coinfections with M. synoviae result in extreme medical signs, though no correlation has been detected between M. synoviae and G. anatis up to now.
Outcomes of this research confirmed statistically vital correlation (p=0.032) within the prevalence of G. anatis and M. synoviae (Determine 1B), which confirms the doable hyperlink between the studied pathogens. G. anatis was detected in nearly all flocks and confirmed greater titers per pattern than M. synoviae, usually (Desk 1), which is in favor of the truth that G. anatis is a commensal microorganism within the higher respiratory system the place it may be present in a excessive quantity with out inflicting a medical an infection. There was no correlation between the portions of the pathogens within the samples. To our data, there have been no medical manifestations of infections on the time of sampling on any of the studied farms.
 Immunoprophylaxis is among the most vital technological measures within the prevention of poultry illnesses. Reside attenuated M. synoviae vaccine confirmed excessive efficacy within the prevention of the medical infections and elimination of the wild strains on farms. Alternatively, G. anatis strains are characterised by excessive genetic variability, which complicates the manufacturing of a common business vaccine, though completely different immunogens are being investigated as doable vaccine candidates. The outcomes of this research confirmed a excessive prevalence of each G. anatis and M. synoviae, and confirmed the necessity for normal monitoring on poultry farms. Since M. synoviae most steadily causes subclinical infections, the pathogen is usually longitudinally unfold by way of the flocks inside a farm, which results in financial losses. Implementation of the sufficient strategies for early detection and management of the bacterial pathogens on poultry farms can result in higher prevention of the illnesses, which is able to lead to more healthy flocks and improved manufacturing charges.
Immunoprophylaxis is among the most vital technological measures within the prevention of poultry illnesses. Reside attenuated M. synoviae vaccine confirmed excessive efficacy within the prevention of the medical infections and elimination of the wild strains on farms. Alternatively, G. anatis strains are characterised by excessive genetic variability, which complicates the manufacturing of a common business vaccine, though completely different immunogens are being investigated as doable vaccine candidates. The outcomes of this research confirmed a excessive prevalence of each G. anatis and M. synoviae, and confirmed the necessity for normal monitoring on poultry farms. Since M. synoviae most steadily causes subclinical infections, the pathogen is usually longitudinally unfold by way of the flocks inside a farm, which results in financial losses. Implementation of the sufficient strategies for early detection and management of the bacterial pathogens on poultry farms can result in higher prevention of the illnesses, which is able to lead to more healthy flocks and improved manufacturing charges.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the farmers for his or her cooperation relating to sampling.
References can be found on request
From the Proceedings of the 70th Western Convention Illness Convention 2021

