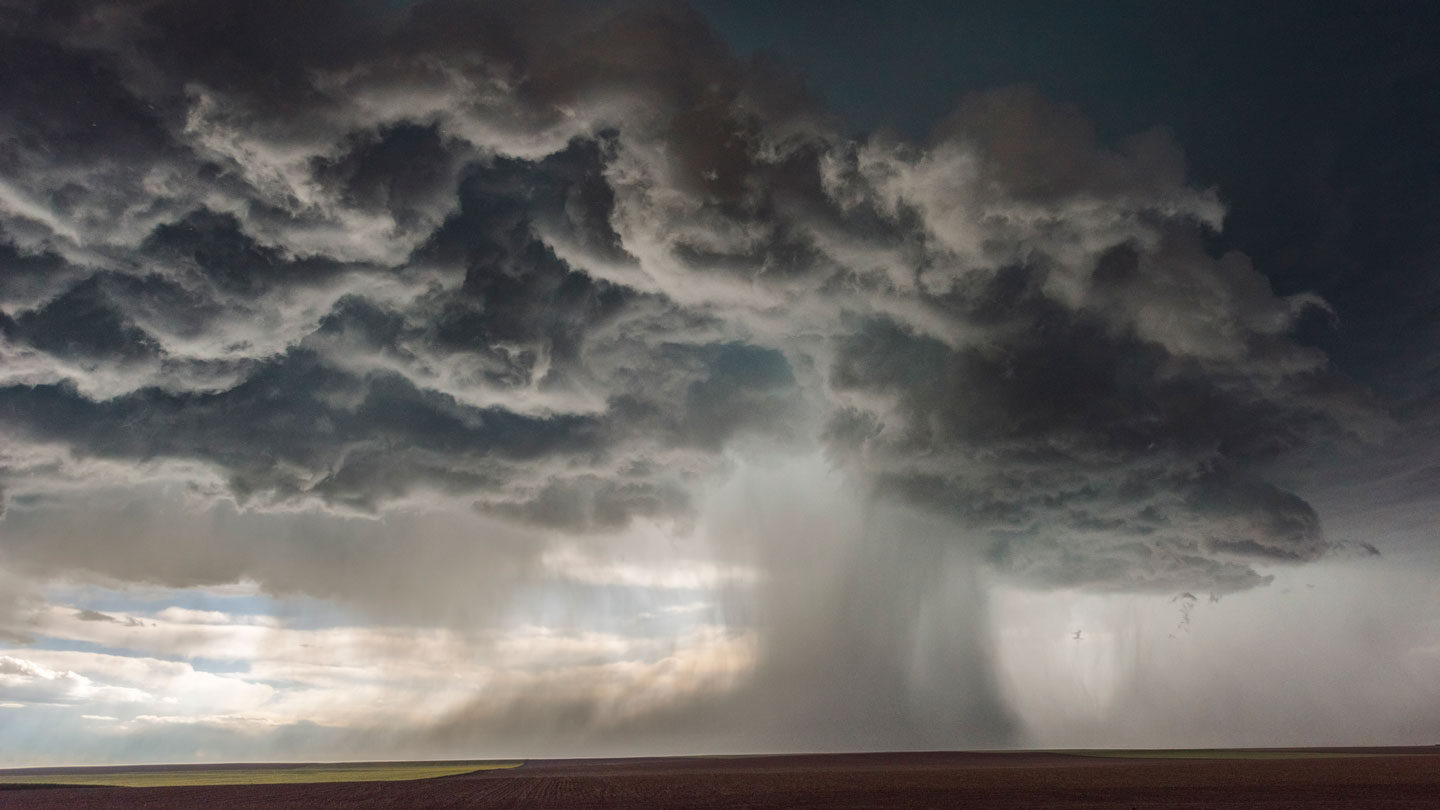
In July, a fierce thunderstorm raged by Washington, D.C., damaging properties, felling bushes, producing blinding rain and leaving hundreds with out energy. The storm was the District’s worst since a derecho swept by the Midwest and Mid-Atlantic areas in 2012 (SN: 8/27/20). Was the brand new harm the results of one other derecho or a twister? No, stated space meteorologists. This time the perpetrator was a downburst.
These lesser-known merchandise of extreme storms first sparked U.S. public consideration within the Nineteen Eighties when one precipitated an airplane to crash close to Dallas-Fort Price Worldwide Airport, killing 137 folks (SN: 3/21/87). Threats to plane have diminished due to extra analysis on the phenomenon and better monitoring of wind speeds at airports. However these fierce winds nonetheless pose a hazard, evidenced by the harm left within the wake of extreme storms which have battered the US and elements of Europe this summer season.
Right here’s what to learn about downbursts.
What are downbursts?
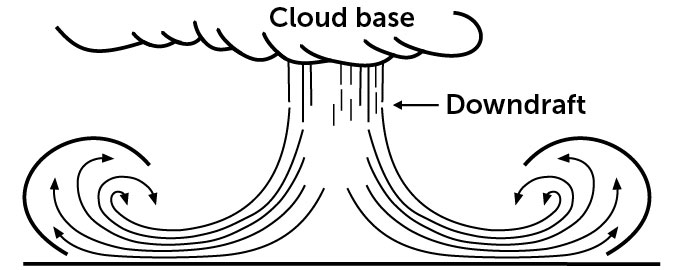
A downburst is an space of highly effective winds produced by a storm with robust downward-moving air, referred to as a downdraft. When the downdraft reaches the bottom, it slams into the floor and spreads out, sending winds outward in all instructions like a water balloon dropped from the sky.
Each storm has a downdraft which sends chilly air towards the bottom and alongside the floor, says Charles Kuster, a analysis meteorologist on the Nationwide Extreme Storms Laboratory in Norman, Okla. However for that downdraft to create a downburst, it wants to achieve a sure velocity. There are a number of completely different thresholds in use, however a standard indicator is wind speeds above 93 kilometers per hour (58 miles per hour), which can be the wind pace that deserves a extreme thunderstorm warning from the Nationwide Climate Service.
Downbursts can are available in two varieties: microbursts, which have an effect on an space smaller than 4 kilometers huge, and macrobursts, which have an effect on a bigger space.
How do downbursts type?
Downbursts want two issues to type: a positive storm atmosphere and a robust cooling mechanism. Humidity that will increase with altitude and a big temperature distinction between the storm and the encompassing atmosphere each create favorable situations for a downburst, as does excessive precipitation loading — the quantity of rain or hail being held aloft by upward winds feeding into the storm.
The cooling mechanism can take a number of completely different varieties. Melting hail or evaporating rain within the environment can cool the encompassing air as a result of these processes require vitality. Djordje Romanic, an atmospheric scientist at McGill College in Montreal, likens this cooling impact to stepping out of a scorching bathe. “You run throughout the room to get your towel, and also you’re chilly, however you simply took a heat bathe,” he says. “It’s doable as a result of that water is evaporating, and evaporation takes vitality” within the type of warmth. The mass of dense, cooled air finally turns into too heavy for the upward winds to maintain it aloft and it falls to the earth, making a downburst.
Downbursts don’t require rain, although. Whereas “moist” downbursts are widespread throughout the southern United States, much less humid western states extra typically expertise “dry” downbursts. In sure instances, rain evaporates within the dry environment earlier than it hits the bottom, cooling the air contained in the storm.
How is a downburst completely different from a twister?
Usually when a downburst strikes, affected residents ascribe the harm to a twister — and one might be forgiven for the error. Downbursts can generate winds which might be about as highly effective as a weak twister, Romanic says. However the parallels finish there. A twister’s attribute funnel cloud requires excessive wind shear — adjustments in wind pace or path at completely different altitudes — to drive its rotation (SN: 12/14/18). Against this, downbursts require low wind shear to maintain from tearing the blob of lofted, cooler air aside.
Patterns of injury differ between the 2 as effectively, says Mark Rose, a meteorologist on the Nationwide Climate Service in Nashville. A twister’s rotating winds will ship particles in a swirling sample, whereas the straight-line winds of a downburst are likely to trigger harm alongside a single path.
Can downbursts be predicted?
Any space that has thunderstorms can encounter a downburst, although not each storm will produce these robust winds, Kuster says. As a result of downbursts “develop rapidly and dissipate rapidly,” he says, the damaging winds can strike with little to no warning.
Storms with the potential to provide downbursts might be detected by radar, which exhibits the placement and the approximate pace of a storm’s most intense winds, Rose says. However as a result of the radar grid is bigger than a typical downburst, it’s troublesome to foretell precisely when and the place a downburst will strike, Romanic says. Most reported downbursts are microbursts, he and colleagues reported in Climate and Local weather Extremes in 2022.
The Nationwide Extreme Storms Laboratory is learning a kind of radar know-how referred to as phased array radar that would detect indicators of an imminent downburst minutes earlier than the downburst hits most depth, probably giving folks within the affected space a number of additional moments to organize.
Will downbursts worsen with local weather change?
It’s arduous to say. Experiences of downbursts have elevated through the years, however Romanic cautions that a lot of that enhance might be tied to enhancements in detection by way of radar, and to the better potential for harm as cities have grown. After accounting for these elements, there hasn’t been a major enhance in downbursts for the reason that Nineties, he says.
However that doesn’t imply additional warmth has no impact on downbursts. Something that will increase a storm’s vitality will increase the chance of extreme winds, Kuster says. That features increased temperatures and extra humidity. As summers get hotter, the planet might see extra storms with the potential to provide downbursts, researchers suspect.
For now, Kuster emphasizes that whereas downbursts will not be as widespread as a typical thunderstorm or as well-known as a twister, they’re nonetheless hazardous. “Downbursts are critical. Extreme thunderstorm warnings are critical,” he says. “So while you go beneath a extreme thunderstorm warning, just be sure you take shelter.”