Half a century in the past, the primary genetically modified organism ushered in a brand new period of organic innovation. To mark this anniversary, listed here are eight milestone GMOs. Many have had, or are poised to have, a dramatic affect on our lives.
1. Escherichia coli
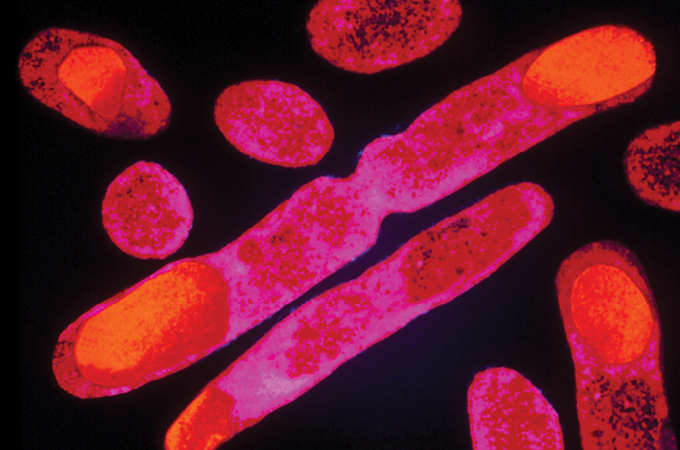
In November 1973, geneticist Stanley Cohen and colleagues reported that that they had constructed a plasmid, a hoop of DNA, that carried a gene from one other organism into an E. coli cell — the delivery of genetic engineering (SN: 6/1/74). The staff later confirmed that such modified cells might produce the protein related to a overseas gene. E. coli has since been modified to mass-produce therapeutic medicine, break down plastics and extra. “An important GMO is the microbes which are used to make insulin,” says geneticist Matthew Cobb of the College of Manchester in England. In 1978, dealing with issues with insulin derived from pigs and cows, scientists engineered E. coli to make human insulin for treating diabetes (SN: 9/16/78). The lifesaving drug hit the market in 1982 (SN: 10/9/82).
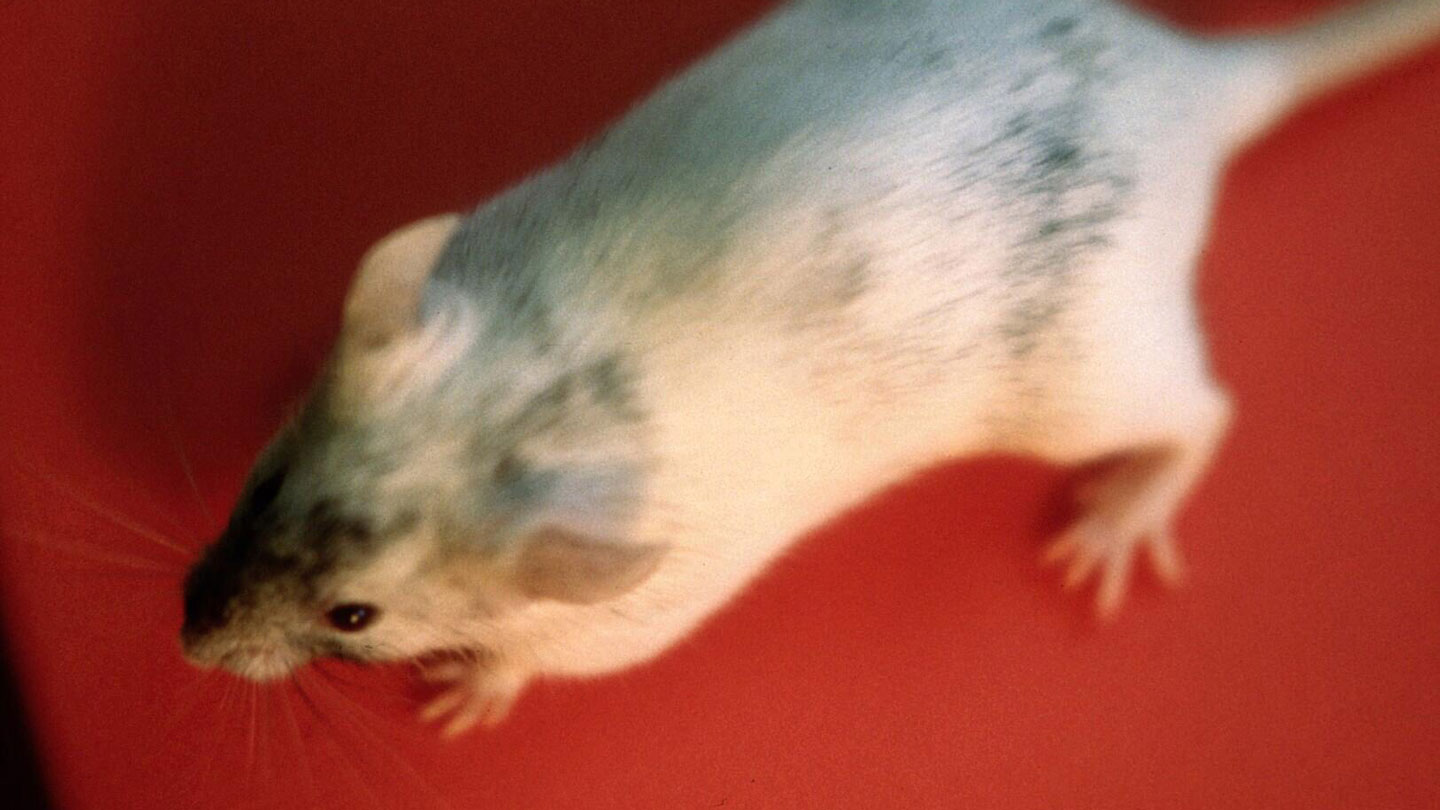
2. Transgenic mice
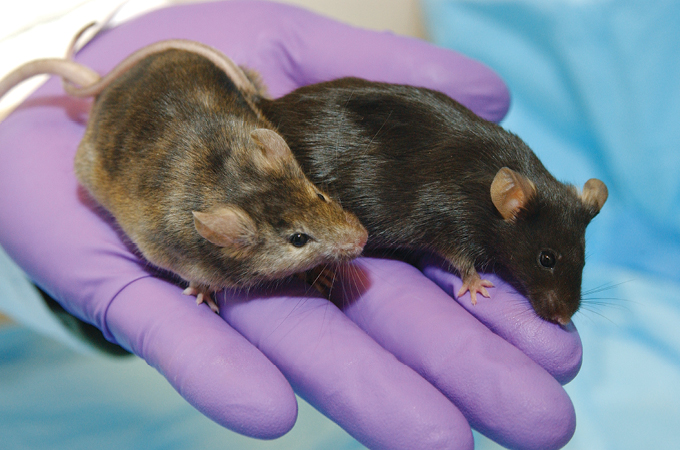
Mouse fashions are a go-to for scientists who wish to research human illness in a managed method within the lab. In 1974, biologists Rudolf Jaenisch and Beatrice Mintz laid the groundwork for these fashions by injecting DNA from simian virus into mouse embryos, which have been later born with viral DNA of their genomes. In papers revealed in 1980 and 1981, a staff led by biologists Jon Gordon and Frank Ruddle included viral DNA into mouse genomes in order that it was handed on to subsequent generations (SN: 9/13/80). The star rodents have been known as “transgenic” mice. Since then, transgenic and knockout mice, the place a single gene is damaged or eliminated, have been developed to imitate and research human illnesses from Alzheimer’s to alcoholism to melancholy and most cancers.
3. Bt tobacco and extra
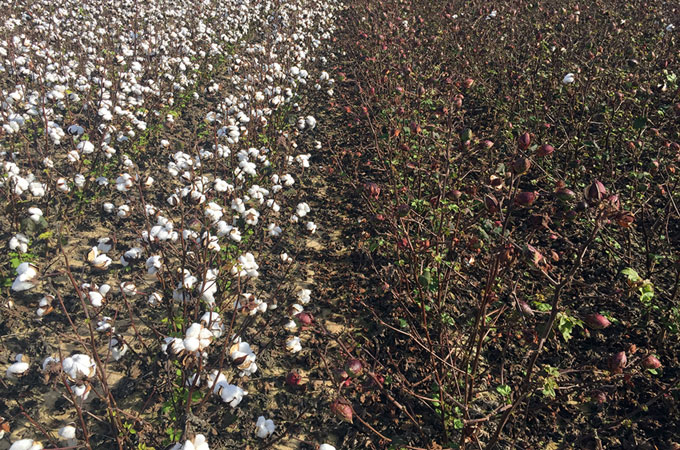

In 1987, geneticist Mark Vaeck and colleagues reported that that they had genetically engineered tobacco to supply Bt toxins. These toxins, made by the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis, have an effect on solely sure bugs, together with a number of frequent agricultural pests. Pesticides derived from the toxins take money and time to spray, however the brand new tobacco plant had built-in safety. Estimates counsel that greater than 1 billion hectares of Bt crops — corn, cotton, soybeans and extra — have been grown since, with no identified issues of safety for customers. These crops have improved yields whereas decreasing the necessity for pesticides. They “are grown on large scales, in lots of international locations around the globe,” says Emma Kovak, a meals and agriculture analyst on the Breakthrough Institute, an environmental suppose tank in Berkeley, Calif. “They’ve had a large affect.”
4. Flavr Savr tomato
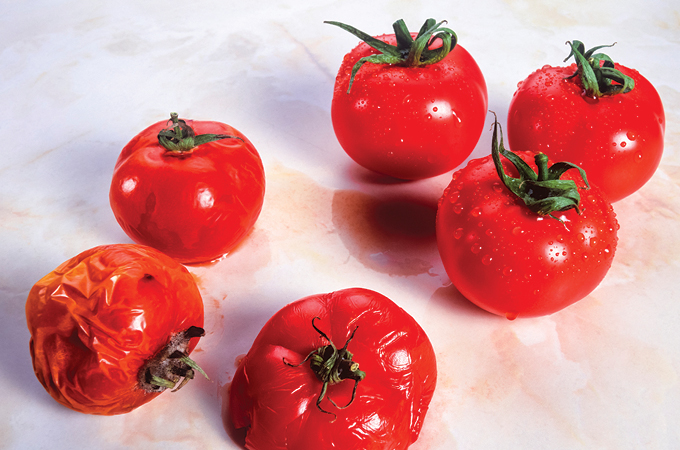

The affect of the Flavr Savr tomato, launched in 1994, is essentially symbolic (SN: 5/28/94). Its genome was modified to dam the manufacturing of an enzyme chargeable for fruit softening, thus retaining the fruit agency longer. Excessive manufacturing and distribution prices in the end doomed the Flavr Savr, however it was the primary genetically engineered crop to be authorized by the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration and to be commercially offered. GM crops have boomed because the Flavr Savr flopped. In 2019, greater than 190 million hectares have been planted with GM crops. Such crops embody potatoes, squash, sugar beets, papayas and corn.
Some folks additionally hint an increase in GMO opposition again to the Flavr Savr tomato, Kovak says. The tomato went via intense security checks, however folks against GMO meals extra typically, then and now, level to potential well being and environmental dangers.
5. Biofortified rice
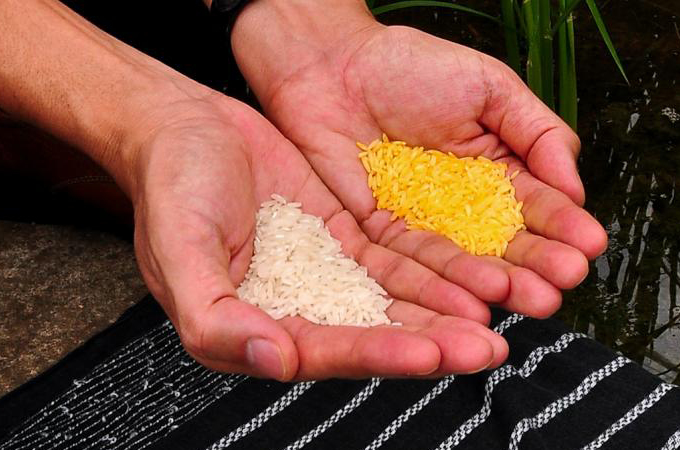

Greater than 2 billion folks worldwide face micronutrient deficiencies. Conventional breeding and genetic engineering can amp up these vitamins, and rice has been an apparent goal. “Greater than half of the world’s inhabitants, together with a lot of these residing in poverty, depend on rice for many of their every day energy,” says B.P. Mallikarjuna Swamy, a rice biofortification researcher on the Worldwide Rice Analysis Institute in Los Baños, Philippines.
Golden rice, developed within the late Nineties by a staff led by biologists Ingo Potrykus and Peter Beyer, incorporates genes from a daffodil and a soil bacterium that allow it to supply a precursor to vitamin A. Meals security regulators have authorized it in the US, Australia, Canada and New Zealand, and it was not too long ago authorized for business use within the Philippines. Regardless of its promise, although, golden rice has not but seen widespread adoption as a result of regulatory hurdles and GMO opposition.
6. AquAdvantage salmon
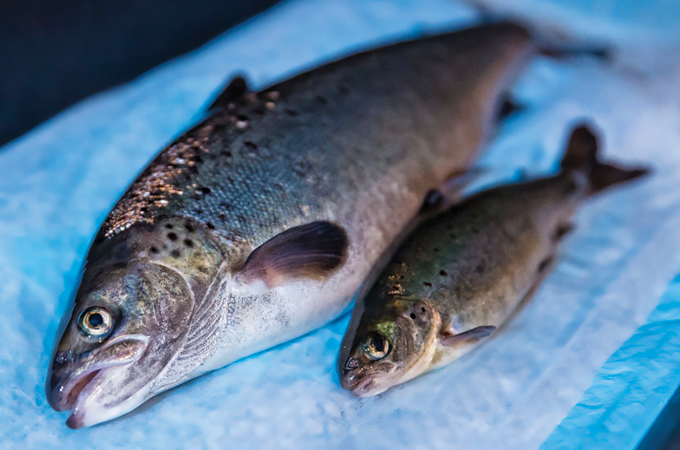

The FDA authorized AquAdvantage salmon for human consumption in 2015 — making the salmon the primary GMO animal to be OK’d as human meals in the US. Canada adopted in 2016. With a progress hormone gene from Chinook salmon, AquAdvantage salmon attain full dimension in half the time of conventional farm-raised Atlantic salmon. Quick-growing farmed salmon might have widespread enchantment, however there are considerations that if the engineered salmon escape, they might push out wild salmon. For now, AquAdvantage salmon are solely trickling into the U.S. provide chain.
7. American chestnut
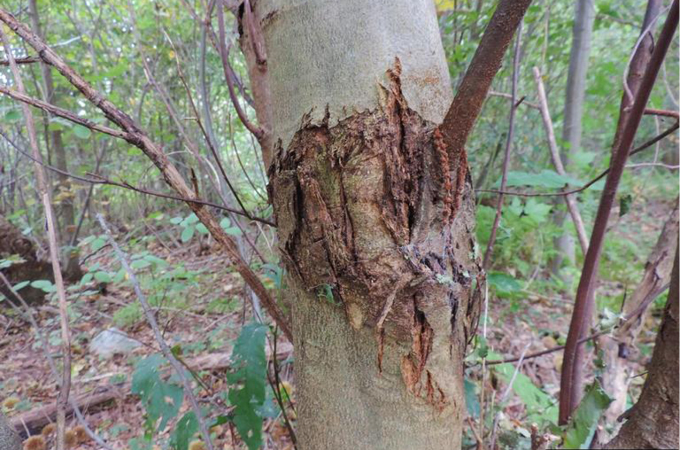

Some researchers are turning to GMOs for conservation. The American chestnut, which as soon as dominated the japanese seaboard, affords an early instance of what such efforts may seem like. These “redwoods of the East” have been severely diminished by the mid-1900s by a parasitic fungus launched from imported timber. Historic efforts to develop a blight-resistant chestnut utilizing conventional breeding haven’t panned out, however the Darling chestnut is perhaps the reply. This genetically engineered tree is extra immune to the fungal blight illness due to a wheat gene that breaks down the dangerous chemical the pathogen produces. The tree has been underneath assessment by regulatory companies since January 2020. After approval, the American Chestnut Analysis and Restoration Challenge on the State College of New York Faculty of Environmental Science and Forestry in Syracuse plans to start out distributing it to restoration packages and the general public.
8. Mosquitoes
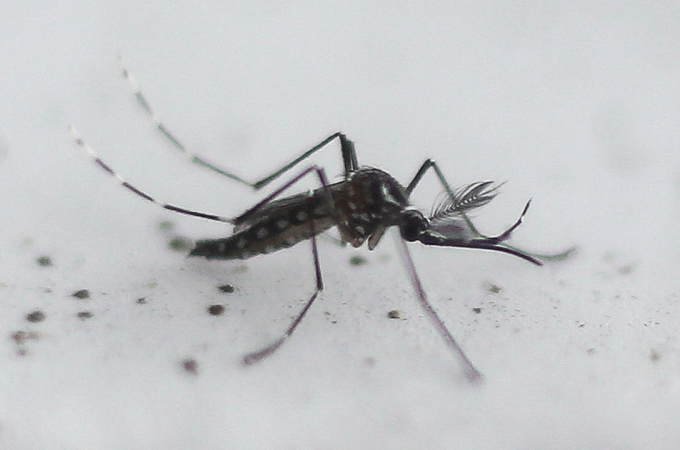

Genetically modifying animals that unfold illness, together with mosquitoes, might save a variety of lives; malaria alone kills lots of of 1000’s of individuals every year. “We’re already utilizing genetically modified mosquitoes for illness management,” says biologist Vanessa Macias of the College of North Texas in Denton. Checks in 2021 in Florida, for instance, launched male Aedes aegypti mosquitoes genetically engineered so feminine offspring die earlier than maturity (SN: 5/14/21). The purpose? Cut back the inhabitants of bugs that unfold the Zika and dengue viruses. Modified mosquitoes have additionally been launched in Brazil, the Cayman Islands, Panama and India.
Different analysis groups are including genes that make mosquitoes immune to a pathogen, says Macias, thereby stopping illness unfold. And advances in gene modifying imply it’s now doable to make use of what are often known as gene drives to unfold genetic modifications via complete populations (SN: 12/2/15). But open questions stay, together with whether or not it’s moral or sensible to rework complete animal populations (SN: 6/3/22). “We’re speaking about unknown unknowns,” Macias says.

