
Rising temperature and consequent adjustments in local weather adversely affect plant progress and growth, leading to lack of wheat productiveness. Excessive environmental temperature could affect crops in numerous methods and such impact varies relying on the crop’s genotype and phenological levels.
A. Khoddami1, V. Messina1, D. Tan1, R. Trethowan1, R. Thistlethwaite1, P. Selle2 and S. Liu1,2
1 The College of Sydney, Plant Breeding Institute, Sydney Institute of Agriculture, Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences, College of Science, Sydney NSW 2006, Australia
2 The College of Sydney, Poultry Analysis Basis, Camden NSW 2570, Australia
The goal of the current analysis was to review the contributions of genotypes, and 12 months of sowing and their interplay on the physico-chemical high quality of wheat cultivars. 4 wheat cultivars, EGA Gregory (E), Lancer (L), Trojan (T) and Borlaug 100 (B) have been sourced from Narrabri throughout the 2019 and 2020 rising seasons. Starch, protein, viscosity, and mineral contents (P, Ca, Na and Okay) have been analysed. The information confirmed that starch, and mineral contents and viscosity have been considerably impacted by environmental issue (12 months) and genotype. Nonetheless, the interplay of 12 months and genotype didn’t present any vital adjustments on the standard of examined grains.
Introduction
Wheat is the predominant feed grain in Australia and different dry areas on this planet. Typical broiler diets in Australia include 60-70% wheat. Local weather-induced elements, together with elevated temperature, have been reported as miserable crop manufacturing across the globe throughout the previous couple of many years and there may be restricted understanding of how climate-induced elements could affect the dietary high quality of wheat.
The sowing time of wheat is crucial issue for temperature-sensitive cereals. Late sowing usually depresses grain yield due to the low temperature throughout germination and the high-temperature stress throughout the reproductive stage. Furthermore, a number of authors have reported that local weather elements akin to excessive temperature or excessive rainfall have a big affect on the bodily and dietary high quality of wheat grains akin to grain quantity, dimension, grain weight, hardness and the composition of protein and carbohydrate content material.
The chemical high quality of wheat grain is principally explored by measuring the content material and composition of protein and carbohydrates in response to warmth stress. The protein content material is elevated by warmth stress, significantly throughout the grain-filling interval.
Carbohydrate focus and composition are important measures of grain chemical high quality and have vital implications for the performance of wheat flour. Starch is the primary carbon reserve in wheat, which contains as much as 75% of whole grain dry weight and warmth can inhibit the effectivity of starch biosynthetic enzymes, affecting starch deposition in creating grains. Submit-anthesis warmth additionally alters the amylose and amylopectin ratio in grains, which can affect the pasting properties of wheat flour. The goal of the current examine was to judge the results of the surroundings (12 months), genotype and their interplay on the standard of Australian wheat grain cultivars.
Technique
4 wheat grains cultivars (EGA Gregory (E), Lancer (L), Trojan (T) and Borlaug 100 (B)) have been sourced from crops grown in Narrabri throughout 2019 and 2020. The 2019 harvest skilled greater temperatures in comparison with the grains harvested in 2020. Wheat grains have been milled utilizing a Cyclone Pattern Mill (UD Company Boulder Colorado USA) to a particle dimension of 500 µm and transferred to a small zip-lock bag, saved within the fridge at 4 °C till evaluation.
Whole starch was measured utilizing an assay equipment from Megazyme (Okay-TSTA).
The overall protein content material of milled wheat flour was decided utilizing a nitrogen/protein Vario MACRO Dice analyser (Frankfurt, Germany). Thirty mg of samples have been ready in 12 x 6 mm pressed aluminium capsules. Samples have been combusted with oxygen and nitrogen oxide. The measured nitrogen content material on this methodology was transformed to whole protein content material by making use of a conversion issue of 6.05.
Pasting property was measured utilizing a Fast Visco Analyser (RVA) (Newport Scientific). 3.5 g of the bottom wheat pattern was added to 24.5 g of water and ran utilizing 50 °C as base temperature to 95 °C after which again to 50 °C inside 13 min cycle.
Mineral content material (Ca, Okay, P, and Na) was analysed utilizing a Perkin Elmer Avio Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICPOES). The outcomes are analysed by two- manner ANOVA to examine the affect of genotype, 12 months of harvest and G xY interplay.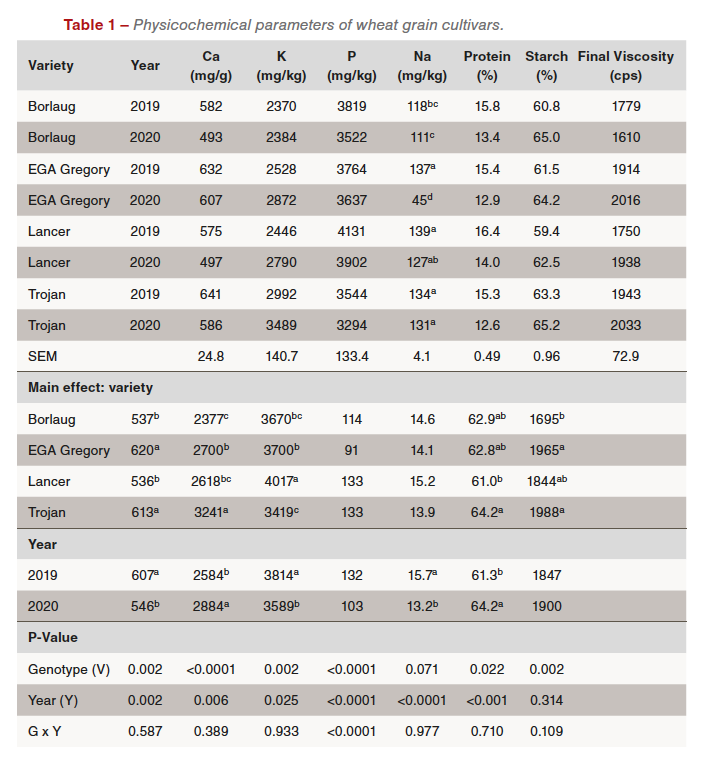
Outcomes
The starch, protein, viscosity, and mineral contents have been decided to examine the affect of the 12 months of harvest, genotypes and their interplay (G x Y) (Desk 1). The affect of 12 months or genotype was vital on high quality attributes of all examined samples. Nonetheless, the obtained outcomes confirmed no vital distinction within the protein content material amongst totally different genotypes (P=0.071). The outcomes additionally indicated that the 12 months of harvest had no affect on the ultimate viscosity of the examined grains (P=0.314).
The starch content material elevated in grains harvested in 2020 whereas considerably greater protein content material was noticed in 2019. The best degree of starch and the bottom degree of protein have been for Trojan.
The outcomes confirmed that the genotype remarkably impacted the RVA last viscosity (P=0.002). The best viscosity belonged to the Trojan.
The outcomes obtained within the experiments confirmed that the mineral content material degree was considerably impacted by all the elements together with, genotype, 12 months and G x Y interplay. Total, the Ca, Na and P contents elevated within the hotter 12 months (2019) whereas the Okay content material decreased.
Dialogue
No matter genotype, the common protein content material elevated considerably in harvested samples in 2019 in comparison with 2020 samples. The pattern is supported by Singh et al. (2021). The starch content material was numerically modified amongst EGA Gregory, Lancer and Trojan. However the starch content material was considerably totally different between the years. The samples from 2019 (hotter 12 months) had the bottom degree of starch.
Plant responses to environmental stress (warmth) throughout grain submitting led to a rise in whole protein content material and reduce in starch biosynthesis and a decrease grain weight. These adjustments within the quantity and high quality of wheat’s main parts could possibly be straight linked to totally different genotypes with totally different genetic backgrounds.
The publicity of the wheat to warmth may affect the protein composition as gliadin manufacturing continues at greater fee than glutenin. This results in a rise within the degree of gliadin and reduces the glutenin content material. The warmth stress additionally influences the amylopectin department chain size and reduces the manufacturing of quick chain branched amylopectin. The warmth stress circumstances may also affect the quantity of soluble NSP which might have an effect on the viscosity. These adjustments within the values might later affect the wheat dough pasting property and energy by growing or reducing the ultimate viscosity.
Mineral content material considerably elevated in 2019 with some exceptions. Helal et al. (2022) reported that a rise in mineral content material in hotter surroundings is a mechanism of warmth tolerance in wheat. Normally, the information exhibits that warmth stress in wheat lowered starch content material and elevated protein and mineral content material.
Acknowledgement: We want to thank the Faculty of Life and Environmental Science on the College of Sydney for offering the fund and help to run the undertaking.
References can be found on request
From the Proceedings of the Australian Poultry Science Symposium 2023
